Introduction
Amidst a global landscape riddled with mounting challenges, the Japanese economy encountered a notable downturn in Q3 of 2023. Initial estimations painted a picture of a 0.5% contraction, but the final figures revealed a 0.7% shrinkage, a stark contrast to the previously revised 0.9% growth experienced in Q2. This downturn marked the first time the GDP faced contraction since Q3 of 2022. The underlying factors driving this decline stem from amplified cost pressures and the formidable headwinds prevailing across the global economic sphere.

Looking deeper into the core components of the economy, both private consumption and capital expenditures witnessed declines. Private consumption, which initially seemed flat, revealed a 0.2% decrease, while capital expenditures faced a more substantial downturn of 0.4%. Moreover, public investment displayed a greater decline than anticipated, marking an alarming 0.8% decrease compared to the initially reported 0.5% fall. This stark contrast followed a notable 1.5% growth in Q2, further emphasizing the volatility within the economic landscape.
The trade landscape also contributed significantly to the overall GDP downturn. While exports managed a modest rise of 0.4%, this paled in comparison to the robust 3.8% growth witnessed in Q2. In stark contrast, imports surged by 0.8%, a significant increase compared to the previous -3.3% figure. These trade imbalances acted as a drag on the GDP, accentuating the vulnerability of the Japanese economy to global shifts and disruptions.
Amidst these challenges, government spending emerged as a beacon of stability, registering a modest increase of 0.3%. This rise, consistent with preliminary figures, contrasts the 0.1% decrease observed in Q2. However, its impact on offsetting the broader economic decline remained limited.
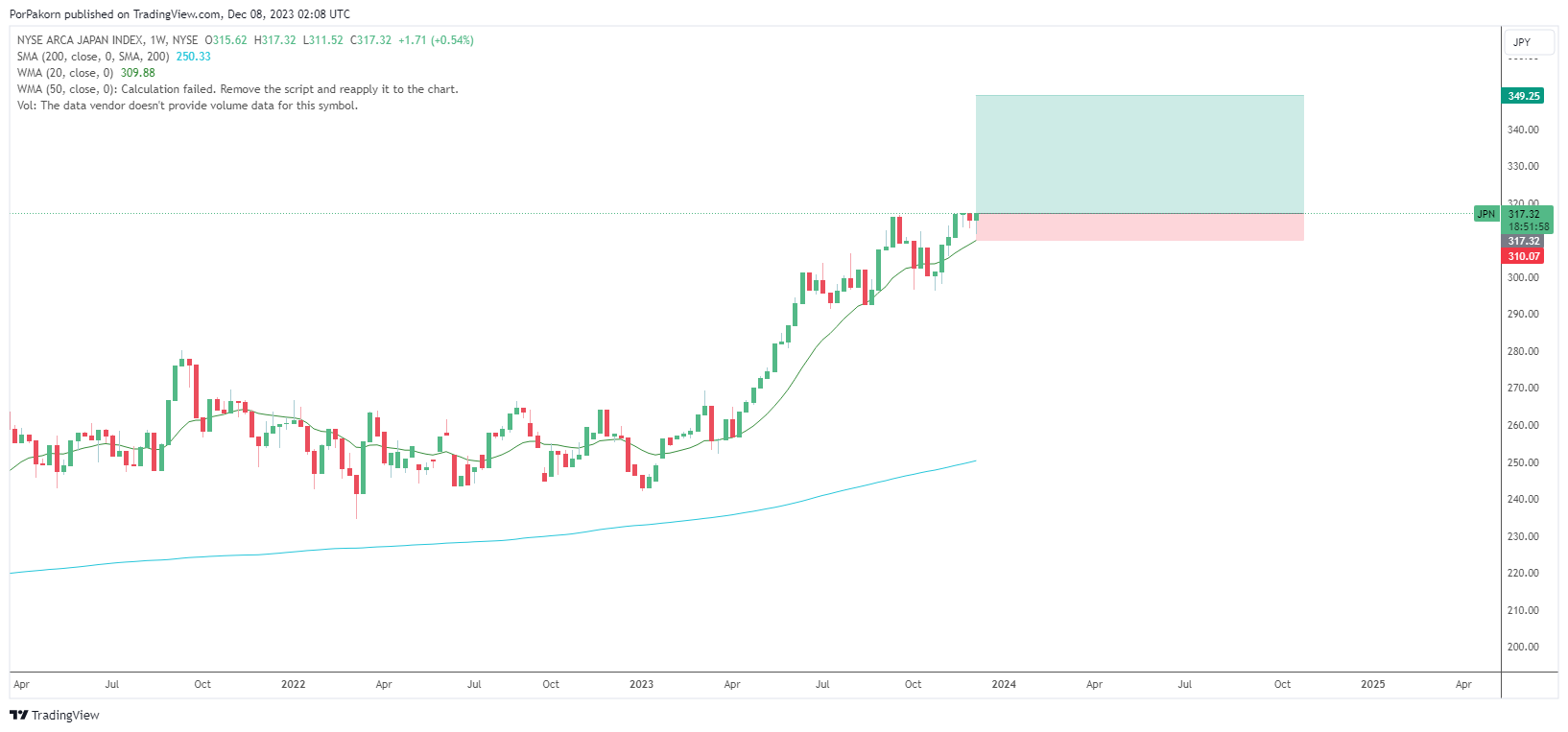
Nikkei Analysis: The Nikkei index, a key benchmark of the Tokyo Stock Exchange, responded sensitively to these economic fluctuations. Observing the intricacies of these GDP trends, the Nikkei reflected a cautious response, displaying fluctuations indicative of the economy’s underlying uncertainties. Investors faced a climate of hesitancy, maneuvering through the volatility of markets impacted by the GDP contraction and its associated factors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Japan’s Q3 2023 GDP contraction highlighted vulnerabilities within the economy, signaling the need for resilience and strategic adaptability in navigating uncertain economic terrains. Amidst global pressures and shifting trade dynamics, prudent financial strategies and government initiatives hold the key to mitigating the impacts of economic contractions, fostering stability, and promoting sustainable growth.