Introduction:
Against the backdrop of a fragile global economy, the American labor market experienced a significant surge in unemployment claims, reaching a staggering 261,000 in the week ending June 3rd, 2023. This surge, which coincided with the Labor Day holiday, marked the wide variety of preliminary jobless claims on account that October 2021, surpassing marketplace expectancies of 235,000. Furthermore, revisions from the previous week showed a slight increase from 232,000 to 233,000 claims. This worrisome trend now extends over three consecutive weeks, indicating a potential weakening in the labor market’s strength. Concurrently, the four-week moving average, designed to eliminate short-term volatility, rose to 237,250, depicting an increase of 7,500 from the preceding week. This article explores the implications of these figures, shedding light on the states most affected and offering insights into continuing claims, while also considering key factors such as the global economy, the Federal Reserve’s actions, the value of the dollar, and trade signals.
The Surge in Initial Jobless Claims:
The sudden surge in initial jobless claims during the week ending June 3rd, 2023, sent shockwaves through the economic community, leaving economists and policymakers deeply concerned. This unexpected increase of 26,000 claims compared to the previous week signifies a notable shift from the positive trend of declining unemployment seen earlier this year. It’s a clear indication that the labor market’s path to recovery may be stumbling, demanding a thorough investigation into the factors driving this alarming rise.
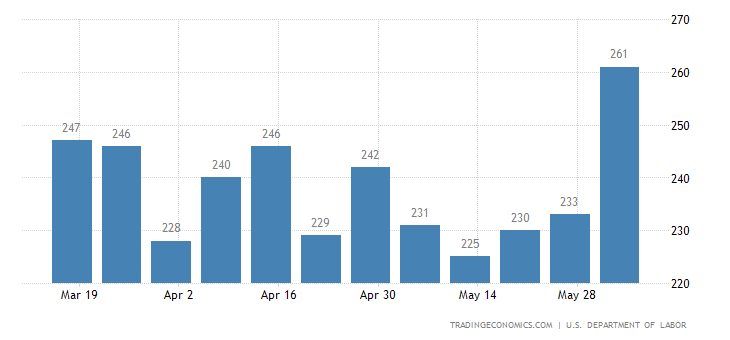
Factors Behind the Increase and Global Economic Implications:
Several factors likely contributed to the sharp increase in initial jobless claims, with implications for the global economy. Firstly, including the Labor Day holiday within the reporting period may have distorted the data, as it often introduces irregularities due to variations in hiring and firing practices. Secondly, the state of the global economy, characterized by uncertainties stemming from trade tensions, inflationary pressures, and supply chain disruptions, may have influenced businesses to adopt a more cautious approach, leading to reduced hiring and, consequently, higher unemployment claims. Furthermore, fluctuations in the value of the dollar, influenced by global economic conditions, can impact trade signals and business decisions, potentially affecting job growth and unemployment rates.
The Federal Reserve’s Role and Economic Outlook:
As the labor market experiences fluctuations amidst the global economic landscape, the actions of the Federal Reserve take center stage. The Fed plays a crucial role in managing monetary policy and has the ability to influence interest rates, which in turn affect borrowing costs for businesses and consumers. By closely monitoring economic indicators, including labor market data, the Fed can make informed decisions to support economic recovery and stability. However, the delicate balancing act of managing inflationary pressures and fostering job growth remains a challenge, requiring a nuanced approach from the central bank.

Geographical Variations in Initial Claims:
Analyzing the unadjusted data, it becomes apparent that certain states experienced more pronounced increases or decreases in initial jobless claims during the reporting period. Ohio witnessed the largest surge, with a staggering 6,345 claims, followed by California, which reported 5,173 claims, and Minnesota, with 2,746 claims. These figures indicate potential localized economic challenges or industry-specific struggles within these regions. Conversely, Connecticut and New York experienced decreases in initial claims, with declines of 2,350 and 1,243 claims, respectively. These disparities suggest varying labor market conditions across different parts of the country, influenced by factors such as global economic dynamics and trade signals.
Continuing Claims and the Path to Recovery:
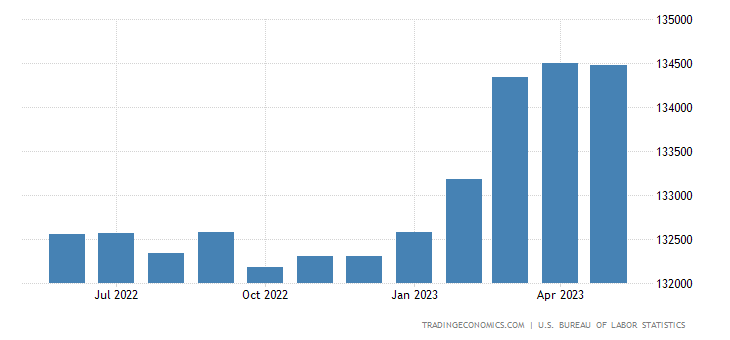
While the surge in initial jobless claims paints a concerning picture, it is essential to consider the data on continuing claims, which reflect individuals who are still unemployed and actively seeking work. Encouragingly, continuing claims decreased from 1,794,000 to 1,757,000 during the reporting period. This decline to the lowest level since mid-February provides a glimmer of hope that individuals are transitioning out of unemployment and reentering the workforce. However, it is essential to exercise caution, as this figure may be influenced by factors such as individuals exhausting their unemployment benefits or withdrawing from the labor force altogether. The path to a robust and sustained recovery hinges on factors such as the global economy, the Federal Reserve’s policy decisions, the value of the dollar, and the resolution of trade signals.
Conclusion:
The recent surge in initial jobless claims, reaching the highest levels seen since October 2021, and the consecutive weekly increases raise concerns about the ongoing recovery of the American labor market in the context of a fragile global economy. Various factors, including the Labor Day holiday, the state of the global economy, and the actions of the Federal Reserve, likely contributed to this sudden rise. By examining the specific states most affected, such as Ohio and California, it becomes evident that localized economic challenges and industry-specific struggles can amplify the impact. As the labor market seeks a path to recovery, the resolution of trade signals, stability in the global economy, the Federal Reserve’s policy decisions, and the value of the dollar will play critical roles in shaping the future trajectory of employment and job growth.






One thought on “Labor Market Fluctuations Amidst a Fragile Global Economy: Fed, Dollar, and Trade Signals”