Introduction: China stock signal
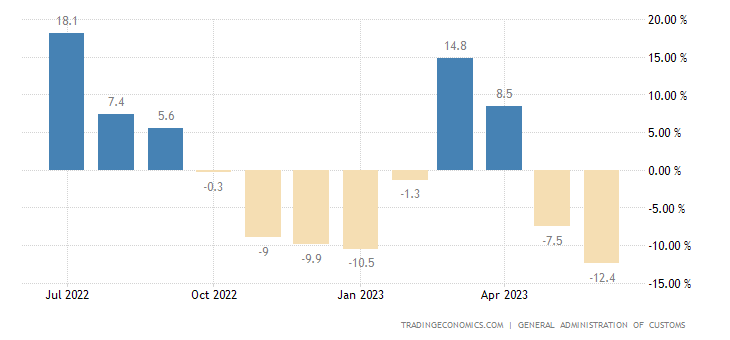
China, the world’s second-largest economy, faced a significant setback in its export performance in June 2023. The latest data reveals a sharp decline of 12.4% year-on-year, amounting to USD 285.32 billion. This drop marks the most substantial contraction since February 2020 and follows a 7.5% fall observed in May. The figures not only surpassed market predictions of a 9.5% decline but also raise concerns about the impact of sluggish global demand on China’s export-oriented economy. This article delves deeper into the factors contributing to China’s export downturn, highlights the sectors affected the most, examines the trade dynamics with major partners, and explores the potential implications for the stock market.
Factors Influencing China’s Export Performance:
The notable decline in China’s exports can be attributed to multiple factors. Slowing global demand has emerged as a primary catalyst, fueled by ongoing uncertainties surrounding the global economic recovery, pandemic-related disruptions, and geopolitical tensions. Weakening consumer sentiment in key markets has curtailed the demand for various Chinese goods, impacting the overall export volume. Moreover, structural shifts in the global supply chain and the implementation of trade policies, such as tariffs and quotas, have further affected China’s export competitiveness.

Sectoral Performance:
Within China’s export portfolio, different sectors experienced varying degrees of impact. Unwrought aluminum and related products bore the brunt of the downturn, with sales plummeting by 18.9%. Similarly, steel products experienced a marginal decline of 0.6%. Another hard-hit sector was grains, witnessing a substantial drop of 36.4%. In contrast, refined products and rare earths managed to buck the trend, registering impressive growth rates of 40.8% and 17%, respectively. Notably, rare earth exports reached 5,009 metric tons, the highest level since March 2020, indicating a potential shift in global demand patterns.

Trade Dynamics with Major Partners:
Analyzing China’s export destinations reveals divergent trends among key trade partners. Exports to the United States, China’s largest export market, recorded a significant decline of 23.7% compared to the previous year. Similarly, exports to the European Union (EU) and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) countries witnessed declines of 12.9% and 16.9%, respectively. These contractions reflect the subdued demand in these markets, influenced by factors like economic uncertainties, changing consumption patterns, and trade tensions. Surprisingly, exports to Russia defied the overall trend, surging by an impressive 90.9%. The disparity in performance across trade partners adds another layer of complexity to China’s export outlook. China stock signal
Implications for the Stock Market:
China’s export slump is likely to have far-reaching implications for the country’s stock market. As a crucial pillar of the Chinese economy, the export sector influences the profitability and growth prospects of numerous listed companies. The decline in export volumes, coupled with reduced revenues, could trigger a downward trend in stock prices. Investors may become cautious and seek alternative investment opportunities, leading to a potential shift in market sentiment. Additionally, the deteriorating export situation may affect supply chain-dependent industries, impacting their earnings and overall market performance. Consequently, it becomes essential for investors and market participants to closely monitor developments in China’s export landscape.
The Link Between China’s Export Performance and Stock Market Volatility: China stock signal
China’s export performance is closely intertwined with stock market volatility. A notable decline in exports can raise concerns about the overall health of the economy, dampening investor sentiment. The stock market tends to be forward-looking, incorporating expectations about future corporate earnings and economic conditions. A slowdown in exports could prompt investors to reassess growth prospects and adjust their investment strategies accordingly. Consequently, a negative correlation between export performance and stock market volatility emerges. Investors should carefully evaluate the impact of export trends on stock market movements to make informed investment decisions.
Conclusion: China stock signal
China’s export contraction during June 2023, the most significant drop since February 2020, has raised concerns about the health of the country’s export-oriented economy. Slowing global demand, structural shifts in the supply chain, and trade policies have all contributed to this decline. Various sectors, including unwrought aluminum, steel products, and grains, experienced declines, while refined products and rare earths managed to grow. The performance varied among China’s major trade partners, with the United States, the EU, and ASEAN countries witnessing declines, while exports to Russia surged. Investors must carefully monitor these developments as they may have implications for the stock market, potentially leading to increased volatility. Evaluating the relationship between export performance and stock market movements is crucial for making well-informed investment decisions in an evolving economic landscape. China stock signal






3 thoughts on “China’s Export Slump: China stock signal”