Introduction
In the dynamic landscape of the global economy, staying well-informed about significant economic indicators is essential for businesses, policymakers, and investors. The China PMI (Purchasing Managers’ Index) serves as a critical barometer for understanding the economic health of the world’s second-largest economy. In October 2023, the Caixin China General Service PMI registered a modest increase to 50.4, up from September’s nine-month low, marking the 10th consecutive month of expansion in the services sector. This development reflects Beijing’s persistent efforts to stabilize its economy.
The gradual easing of travel restrictions played a pivotal role in boosting foreign sales, which witnessed growth for the second consecutive month. These measures attracted more international tourists to the Chinese market. Simultaneously, the employment sector showed signs of stabilization after eight months of continuous growth, providing a semblance of stability within the job market. Additionally, outstanding business orders continued to accumulate at an accelerated rate, reaching the highest levels since January. However, the new orders component of the China PMI presented a contrasting picture, showing the slowest growth rate so far in 2023 due to persistently weak demand.
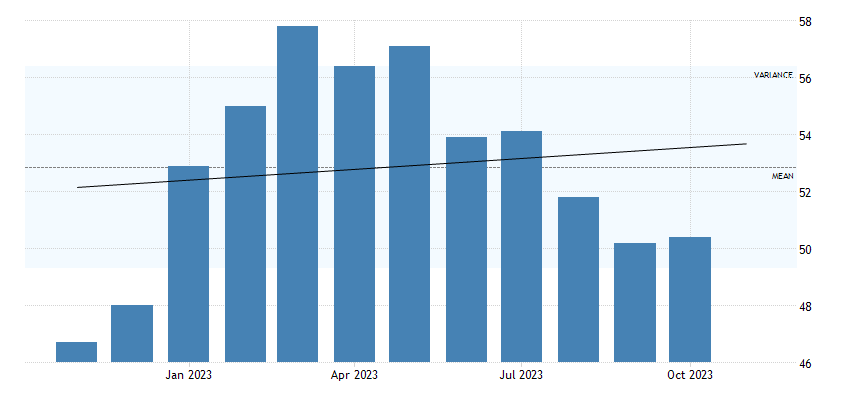
On the cost front, the China PMI revealed intriguing insights. Input price inflation hit its lowest point since June 2022. This decline was attributed to limited increases in the costs of labor, raw materials, and transport, offering a temporary respite from the upward pressure on input prices. Meanwhile, prices charged by firms saw a notable surge, reaching levels not seen since May. These price hikes were driven by firms seeking to pass on the higher input costs to their clients, aiming to safeguard their profit margins.
Despite these positive developments in various segments of the China PMI, there is an undercurrent of caution in the air. Sentiment among businesses appeared to be less upbeat, weakening for the fourth consecutive month and reaching a 3.5-year low. These declining sentiments were fueled by growing concerns about the overall economic outlook. This sentiment downturn hints at uncertainties and challenges that may lie ahead for the Chinese economy.
Transitioning from the specifics of the October 2023 China PMI data, let’s delve deeper into the trends and their implications. The sustained growth in the services sector, as indicated by the rising PMI, is a testament to China’s ongoing commitment to diversify its economic structure. It signifies the nation’s progression from a manufacturing-oriented economy to one that increasingly relies on the services industry as a driver of growth.
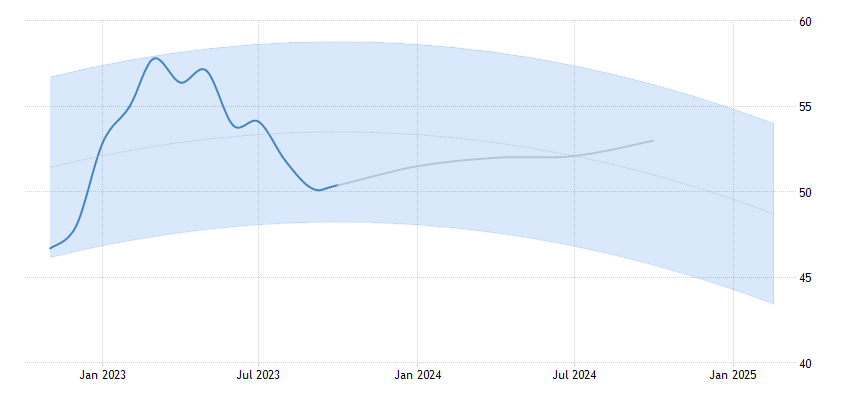
The robust and sustained uptick in overseas sales is a heartening beacon for China’s export-centric enterprises. As the nation unfurls the welcome mat for global sojourners, the vista of surging demand for wares and services widens before us. For discerning investors, this beckons as an opportune moment to delve into firms wielding resolute export connections, particularly those strategically positioned to satiate the impending horde of foreign wanderers.
The attainment of equilibrium in employment carries profound significance for the labor domain. A steady job market wields the potential to bolster the faith of consumers, ushering forth an era of augmented expenditures. Companies entrenched within the domestic sphere should be primed to answer the call of this burgeoning appetite for consumer goods and services, especially within the realms of retail, hospitality, and healthcare.
On the flip side, the slowdown in new orders suggests that domestic demand remains subdued. Businesses need to monitor this trend carefully, and those reliant on local consumption may need to adapt their strategies to navigate these uncertain waters.
Turning our attention to cost dynamics, the decrease in input price inflation comes as a relief for businesses grappling with rising costs. However, it is essential for firms to remain agile and adaptable to sudden cost fluctuations. Cost management strategies, such as supply chain diversification and efficient resource allocation, can help businesses maintain their competitiveness.
The surge in prices charged by firms is indicative of the efforts to protect profit margins amid cost pressures. For investors, this emphasizes the importance of tracking the pricing strategies of companies in their portfolios. Furthermore, consumers may face higher prices, necessitating careful budgeting and spending decisions.
The waning business sentiment reflects growing concerns about the economic trajectory. For investors and businesses, it is a call to stay vigilant and adaptable in the face of uncertainties. To mitigate risks associated with economic uncertainty, diversified investment portfolios and risk management strategies should be considered.
As we march onward, it is imperative to bear in mind that the China PMI is not merely a cold statistical datum; it serves as a portal into the intricate economic intricacies of a worldwide juggernaut. Remaining abreast of the China PMI and deciphering its undulating patterns can prove to be an invaluable instrument for investors, corporations, and policymakers in equal measure. In light of the October 2023 data, we are offered a multifaceted tableau of China’s economic terrain, one that unfurls both promising vistas and formidable hurdles.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the China PMI, with its persistent growth in the services sector, stabilization of employment, and fluctuating cost dynamics, presents a multifaceted view of China’s economic health. While the overall sentiment remains cautious, there are opportunities to be seized, particularly for businesses, investors, and policymakers who can adapt to the evolving economic landscape. Navigating China’s economic waters in 2023 requires a keen eye on the China PMI and a proactive approach to addressing the trends and challenges it unveils.