Introduction
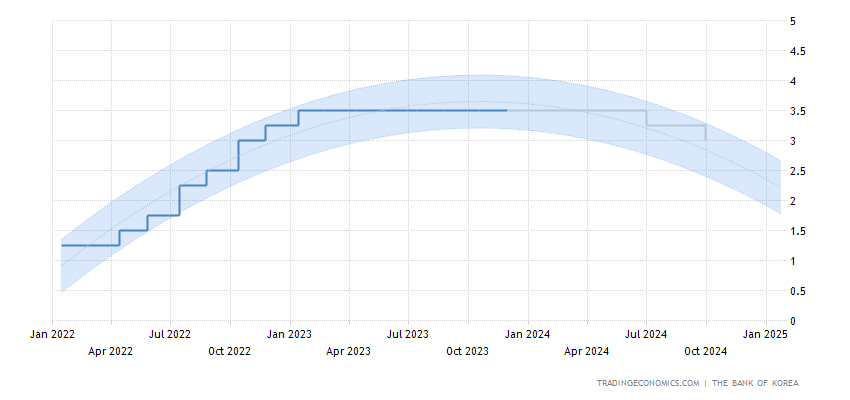
The Bank of Korea, in its anticipated November meeting, upheld the base rate at 3.5%, maintaining a steady trajectory in borrowing costs for the seventh consecutive time. This measured stance aligns with historical patterns, considering that from 1999 to 2023, South Korea’s Interest Rate averaged 2.89%. Notably, it peaked at 5.25% in October 2000 and descended to a record low of 0.50% in May 2020.
Understanding the nuances of the Korea Interest Rate ecosystem is crucial for investors, businesses, and policymakers alike. This pivotal economic lever has profound implications, influencing consumer spending, investment patterns, and overall market sentiment. The consistent hold on the base rate underscores the Bank of Korea’s cautious approach, balancing economic growth and inflation containment.
For investors eyeing opportunities in South Korea, monitoring the Interest Rate trends becomes imperative. A sustained low rate environment often signifies an accommodating monetary policy, potentially stimulating borrowing and investment. Conversely, higher rates may suggest a tightening stance, influencing capital flows and investment strategies.
However, reliance solely on Interest Rate movements might not suffice. External factors, such as global economic shifts and geopolitical dynamics, can significantly impact South Korea’s Interest Rate trajectory. Therefore, diversifying investment portfolios and remaining vigilant amid evolving market conditions are prudent strategies.
In navigating South Korea’s Interest Rate terrain, businesses should adopt a proactive approach. Assessing the potential impact of Interest Rate changes on borrowing costs and consumer behavior becomes paramount. Hedging against rate fluctuations and optimizing financial strategies can mitigate risks and capitalize on favorable market conditions.
Additionally, policymakers must maintain a delicate balance between fostering economic growth and guarding against inflationary pressures. Continual assessment and fine-tuning of monetary policy frameworks are essential to sustain a stable economic environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the stability of South Korea’s Interest Rate at 3.5% signifies a measured approach by the Bank of Korea amid evolving economic landscapes. Investors, businesses, and policymakers must heed the implications of Interest Rate dynamics while adopting proactive and diversified strategies to navigate the ever-changing financial terrain. Understanding the nuances and interplay of various factors will be pivotal in making informed decisions and capitalizing on emerging opportunities in South Korea’s dynamic market.





