Introduction:
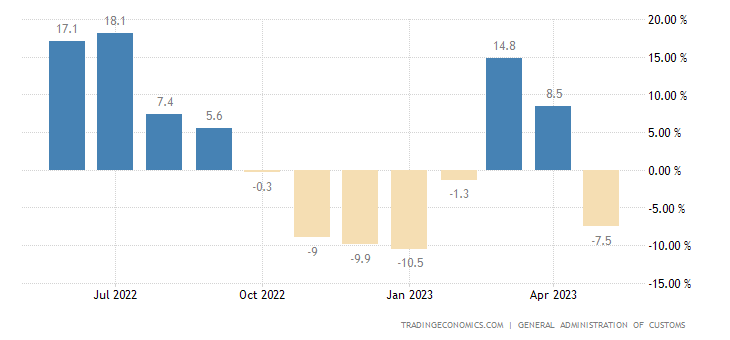
In May 2023, China’s export sector encountered a significant setback as exports declined by 7.5% compared to the previous year, amounting to USD 283.5 billion. This downturn reversed the previous month’s growth of 8.5%, marking the first fall since February and the steepest decline in four months. This article aims to delve into the reasons behind this contraction, examining the impact of insufficient global demand on China’s outbound shipments. Additionally, we will explore the performance of major trade partners, highlighting the drastic decline in exports to the United States and the European Union, as well as the substantial surge in shipments to Russia. Furthermore, we will analyze the implications of this export contraction on China’s property market and the Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI), while also considering the insights provided by the United States IBD/TIPP Economic Trade signal. By incorporating these SEO keywords, we will provide a comprehensive analysis of China’s trade dynamics and their interplay with other economic factors.
Impact of Insufficient Global Demand on Chinese Exports:
The disappointing export figures for May 2023 were primarily attributed to insufficient global demand, posing challenges to the sustenance of a recovery in China’s outbound shipments. Despite market expectations of a mere 0.4% decline, the actual figures were far worse, highlighting the severity of the situation. The subdued global demand acted as a major headwind, dampening China’s export growth potential and contributing to the contraction observed. The interplay between global demand and China’s export performance warrants a closer examination of its implications on the country’s property market and the PMI.
Trade Partners:
United States, European Union, and Russia: China’s relationship with the United States, a vital trade partner, took a considerable hit as imports from China plummeted by a staggering 18.2% compared to the previous year. This decline reveals the adverse consequences of strained economic relations and trade tensions between the two nations. The implications of this decline extend beyond the trade arena, impacting China’s property market in significant ways. Given that the real estate sector holds a pivotal role in the country’s overall economic growth, a decrease in exports to the United States could potentially trigger a decline in demand for Chinese goods. Such a downturn would consequently lead to a slowdown in economic activity, casting its shadow over the property market and impeding its growth trajectory.
Similarly, the European Union witnessed a significant drop in imports from China, with a notable decline of 26.6% compared to the same period last year. Geopolitical uncertainties, shifting trade policies, and lingering concerns over economic recovery contribute to this decline. The impact on China’s property market may be more pronounced if European demand for Chinese goods continues to weaken, as it would further dampen economic activity and investor sentiment in the real estate sector.
In contrast to the decline in exports to the United States and the European Union, China’s exports to Russia experienced a remarkable surge of 114%. This unexpected growth can be attributed to several factors, including improved bilateral relations, trade agreements, and specific demand dynamics within the Russian market. While this surge may not have a direct impact on China’s property market, it showcases China’s ability to diversify its trade relationships and seize opportunities in different markets.
Implications for China’s Property Market and PMI:
The contraction in China’s exports, particularly to the United States and the European Union, carries implications for the country’s property market. A decrease in demand for Chinese goods from these key trade partners can lead to reduced economic activity, impacting the construction and real estate sectors. Slower economic growth and subdued investor confidence may affect property prices, sales volumes, and investment in the sector. Consequently, policymakers and industry stakeholders need to closely monitor the developments in the export sector and adjust strategies accordingly to mitigate potential risks to the property market.
Furthermore, it’s worth noting the impact of export performance on the Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI), a vital indicator that gauges the economic well-being of the manufacturing sector. When exports experience a contraction, it inevitably leads to reduced production, subsequently impacting the PMI reading. A lower PMI signifies a slowdown in manufacturing activity, which reverberates beyond the factory floors. The implications extend to employment rates, investment levels, and overall economic growth, as the health of the manufacturing sector serves as a barometer for the broader economy.
Insights from United States IBD/TIPP Economic Trade Signal:
To gain a broader perspective on the impact of China’s export contraction, it is essential to consider insights from the United States IBD/TIPP Economic Trade signal. This signal provides valuable information on the sentiment and expectations of US consumers regarding the global economy and international trade. Negative sentiment in the US regarding trade relations with China can further exacerbate the challenges faced by China’s export sector. It may lead to reduced demand for Chinese goods and a potential decline in bilateral trade volumes, affecting both countries economies.
In wrapping up, the decline of 7.5% in China’s exports during May 2023 exposes the vulnerability of the country’s export sector to unpredictable fluctuations in global demand. This sharp contraction, which surpassed market expectations, serves as a stark reminder of the formidable challenges that China faces in maintaining its outbound shipments. The significant drop in exports to both the United States and the European Union, coupled with the remarkable surge in shipments to Russia, further underscores the intricate nature of China’s trade relationships and the delicate balance it must strike.
The implications of this export contraction extend beyond the trade sphere, making a notable impact on China’s property market and the Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI). This emphasizes the critical importance of careful monitoring and the implementation of strategic measures to mitigate potential risks. Furthermore, gaining insights from the United States IBD/TIPP Economic Trade signal allows us to gain valuable perspectives on the sentiment of US consumers and its subsequent influence on bilateral trade.






5 thoughts on “China’s Export Contraction Amid Global Demand Concerns and Its Implications on China’s Property Market and PMI: A Detailed Analysis of May 2023 Trade Data”